The buildmaster decides what, when and how the system is build, it has a configuration file called master.cfg where the build process is defined. On the other hand, the buildslaves handle the execution of the commands and return results to the master.
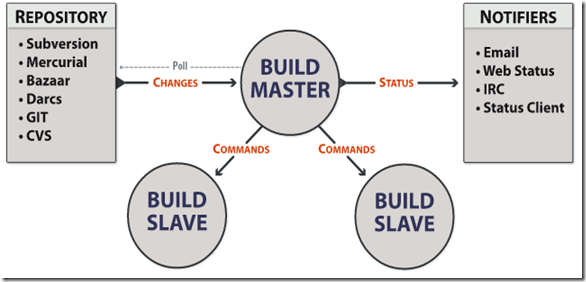
The following is a graph (from buildbot’s wiki) shows buildbot architecture supported repositories and notifiers.
Setting up
To setup on windows, the master and slaves require:
- Python 2.7 http://www.python.org/download/ and setuptools http://pypi.python.org/pypi/setuptools/0.6c11.
- Twisted http://twistedmatrix.com (I’m using 12.1.0 for Python 2.7 64 bits).
- Twisted requires PyWin32 in order to spawn processes on Windows http://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/ (downloaded pywin32-217.win-amd64-py2.7).
- sqlite3: http://www.sqlite.org (sqlite-dll-win32-x64-3071300).
- Jinja2: http://jinja.pocoo.org/ (http://pypi.python.org/pypi/Jinja2/2.6).
- SQLAlchemy http://www.sqlalchemy.org/ (SQLAlchemy-0.7.8).
- SQLAlchemy-Migrate http://code.google.com/p/sqlalchemy-migrate/ (sqlalchemy-migrate-0.7.1.tar)
For this example, I installed both on same machine, if the installation went ok you should be able to check their versions:
The following steps creates and starts the master and slave:
Create BuildbotMaster
C:\Python27\Scripts>buildbot create-master -r C:\BuildMaster
Create BuildbotSlave
C:\Python27\Scripts>buildslave create-slave C:\BuildSlave localhost:9989 BuildSlave01 mysecretpwd
Start BuildbotMaster
C:\Python27\Scripts>buildbot start c:\BuildMaster
Start BuildbotSlave
C:\Python27\Scripts>buildslave start c:\BuildSlave
if everything went fine you should see a page like the following:

You can check for errors on C:\BuildMaster\twistd.log and C:\BuildSlave\twistd.log.
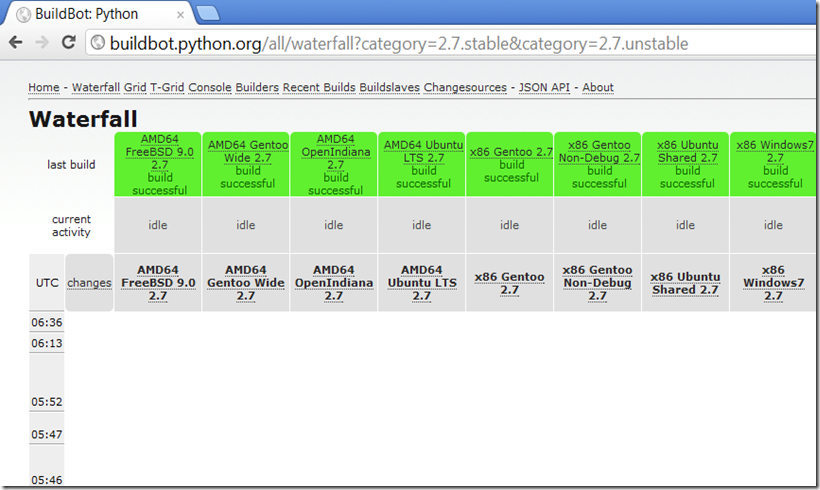
Who is using buildbot: Python, Mozilla, Google Chromium and others. The following shows Python 2.7 waterfall page:
On my next post I’ll show you how to run automated builds and tests for a .net application hosted on git/codeplex using buildbot.
No comments:
Post a Comment